Lecture 35: Consensus I
COSC 273: Parallel and Distributed Computing
Spring 2023
Annoucements
- Quiz Posted Tonight
- Leaderboard 2 Test Results Soon
Binary Consensus
Setup:
- $n$ processes/threads, $P_1, P_2, \ldots, P_n$
- processes have unique IDs, $1, 2, \ldots, n$ (like
ThreadId.get()) - each process $i$ holds input $x_i = 0$ or $1$
Output:
- each process $i$ outputs $b_i = 0$ or $1$
Failure:
- Some process(es) may crash
- failing process may perform some steps before failing
- cannot distinguish slow from crash
Conditions for Consensus
-
Agreement: all processes output the same value
-
Validity: if all systems have the same input, they all output that value
-
Termination: all (non-faulty) processes decide on an output and terminate after a finite number of steps
Exercise
Devise an algorithm for consensus assuming:
- Extremely fair scheduler: all processes take a step before anyone takes a next step
- execution in synchronous rounds
- No faulty processes
- Access to shared array of size $n$
Consensus with Faults
Suppose some process(es) may crash at any time during an execution…
- Other processes can’t tell that a process crashes
- e.g., cannot distinguish slow process from crashed
Not Consensus 1
How can we achieve…
Agreement: all processes output the same value- Validity: if all systems have the same input, they all output that value
- Termination: all (non-faulty) processes decide on an output and terminate after a finite number of steps
Not Consensus 2
How can we achieve…
- Agreement: all processes output the same value
Validity: if all systems have the same input, they all output that value- Termination: all (non-faulty) processes decide on an output and terminate after a finite number of steps
Not Consensus 3
How can we achieve…
- Agreement: all processes output the same value
- Validity: if all systems have the same input, they all output that value
Termination: all (non-faulty) processes decide on an output and terminate after a finite number of steps
So
Without too much trouble, we can achieve…
- …consensus with synchronous rounds, no faults
- …“consensus” without agreement
- …“consensus” without validity
- …“consensus” without termination
What about consensus with faults?
A Remarkable Fact
Theorem (FLP, 1985). There is no algorithm that achieves consensus in the presence of even a single faulty process.
- Proven by Fischer, Lynch, and Paterson in 1985
- their version of result for “message passing” model
- ours is for shared memory with atomic read/writes
- Surprise to the parallel/distributed computing community
- Among most influential results in CS
Our Plan
Prove version of FLP result:
- There is no wait-free protocol for consensus with read/write registers for any $n > 1$
- wait-free means all processes terminate after a finite number of steps independently of other processors’ behavior
- wait-free is a stronger assumption than termination
-
termination just means that all processors halt eventually
- our result is weaker than the FLP result
Computational Model
- Processes have shared memory (registers)
- Atomic read/write access
- behavior like
volatilevariables in Java
- behavior like
- Scheduler decides which process makes a step
- assume each step is read/write
- Some processes may crash
- such a process is never scheduled again
- Scheduler is otherwise fair: non-crashed processes are scheduled eventually
Algorithms
An algorithm $A$ specifies next operation:
- read value from shared register
- write value to shared register
- terminate
as a function of
- input ($x_i$)
- outcomes of previous (read) operations
Next step is uniquely determined by local input and values read in previous steps
Example: Default to 0
Idea: output 0 unless all processes have input 1
int in = getLocalInput();
int i = ThreadId.get();
write(i, in); // write my value to register i
if (in == 0) return 0;
for (int j = 0; j < nProcesses; j++) {
// wait until register j has been written
while (read(j) != 0 && read(j) != 1) { };
if (read(j) == 0) return 0;
}
// all processors have in == 1
return 1;
Executions
An execution $E$ of algorithm $A$ specifies
- Inputs of all processes
- Sequence of steps taken by processes
- read
- write
- terminate
- crash
Executions may be incomplete
- Not all nodes have terminated/crashed yet
- encodes current state/history of execution
Executions may be extended by scheduling more steps
Example of Execution $E$
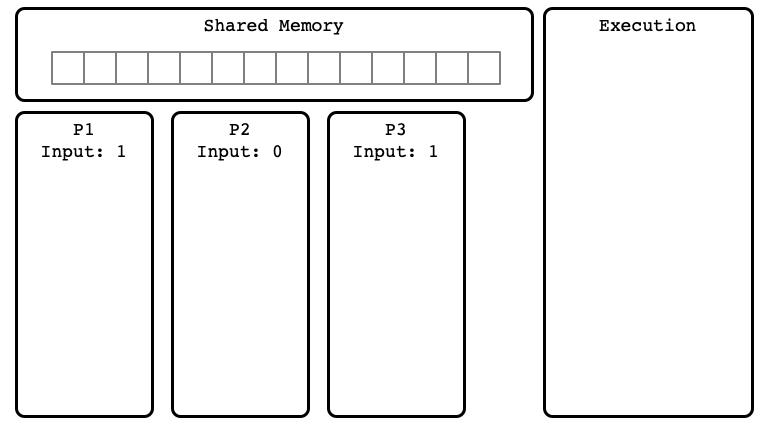
$E$ Step 01
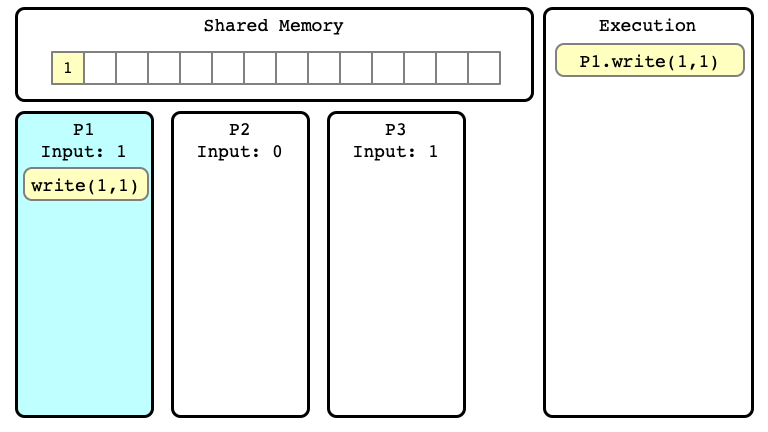
$E$ Step 02
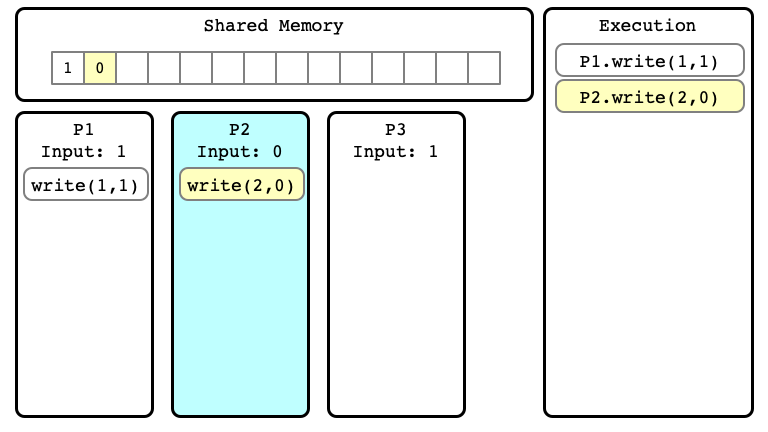
$E$ Step 03
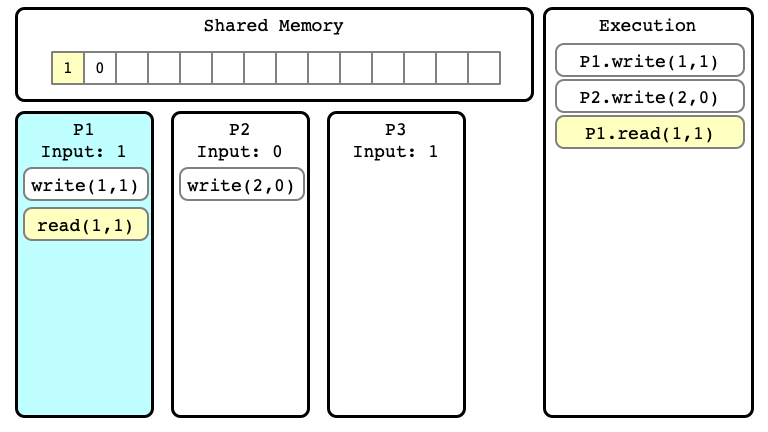
$E$ Step 04
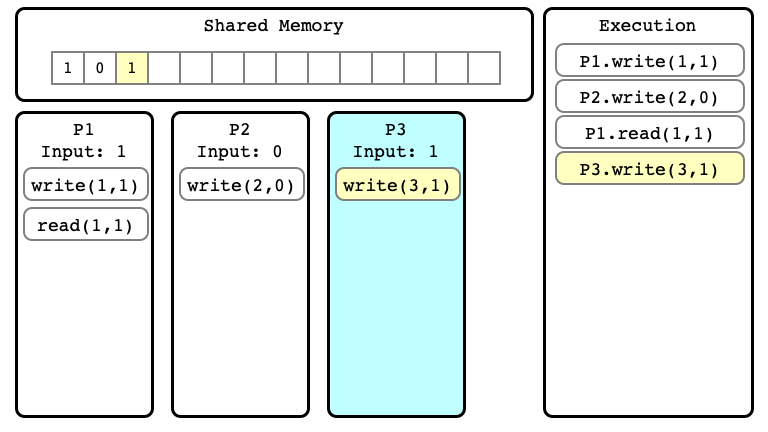
$E$ Step 05
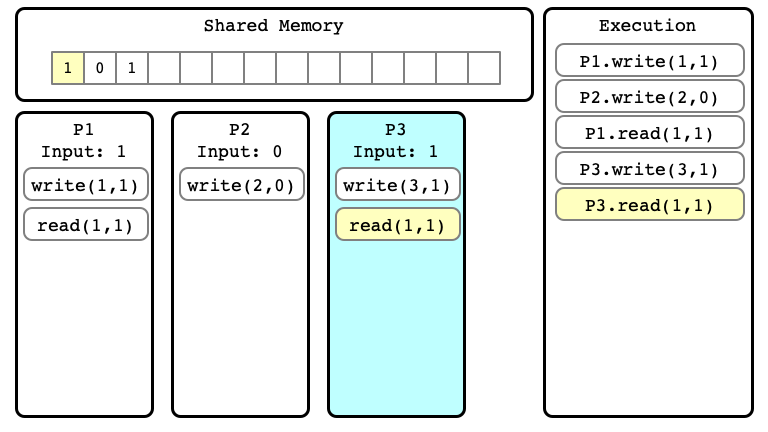
$E$ Step 06
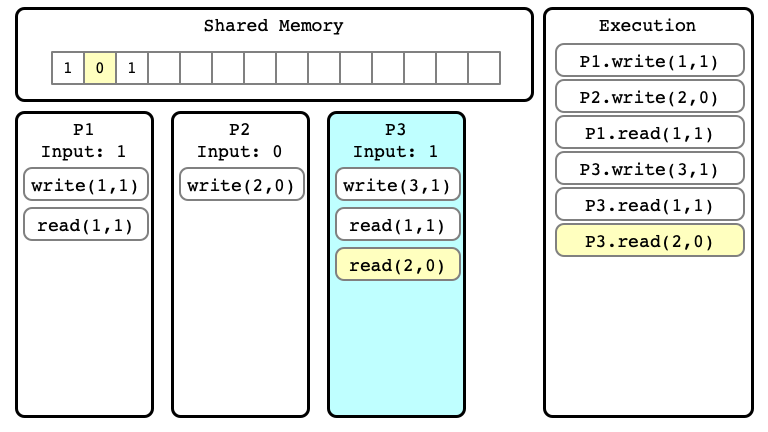
Extending Executions
In $E$, no process has terminated yet
- We can consider extensions of a given execution
- Start with $E$, and perform more steps
$E’$ Step 06

$E’$ Step 07
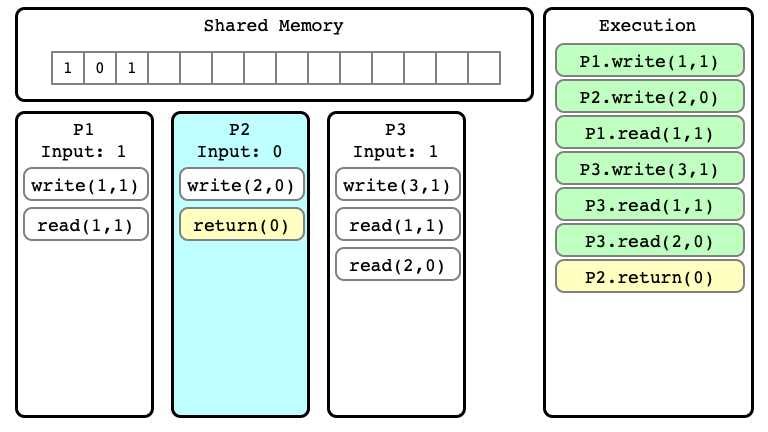
$E’$ Step 08
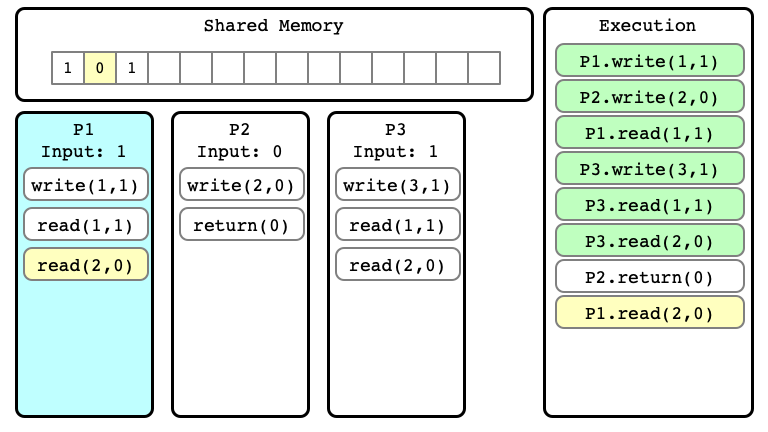
$E’$ Step 09
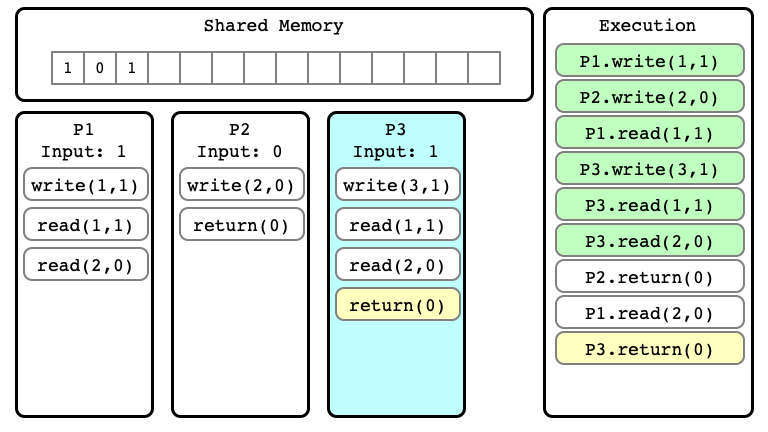
$E’$ Step 10
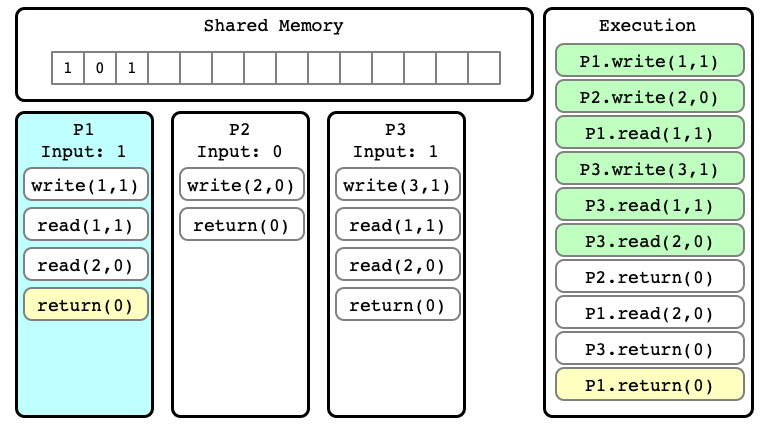
Note
We can consider many different extensions of $E$
Extension $E’$ of $E$

Alternate extension $E’’$
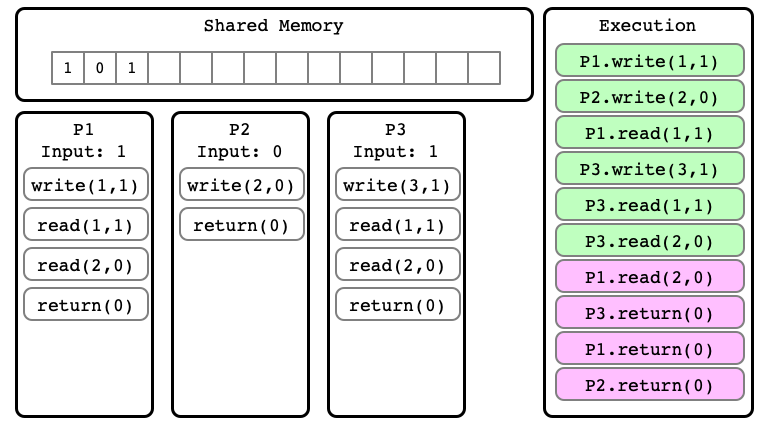
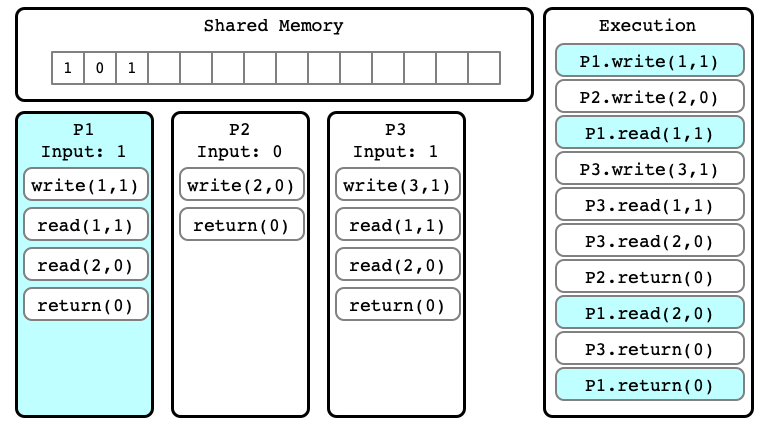
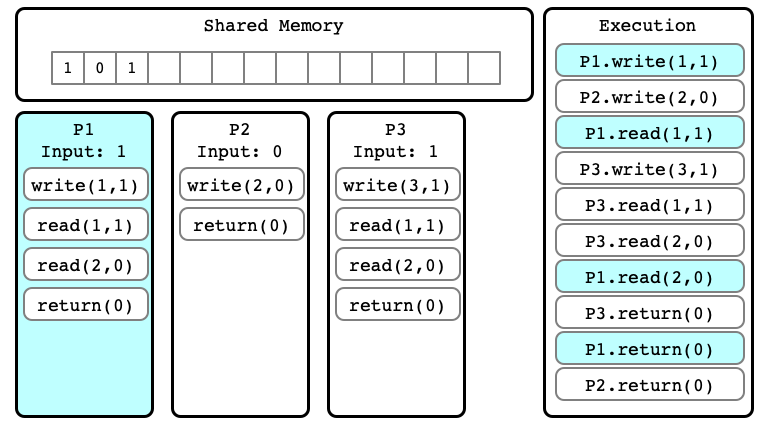
Indistinguishable Executions
- $E$ and $E’$ are executions
- they are indistinguishable at process $P_i$ if in $E$ and $E’$:
- $P_i$ has same input
- sequence of read/write operations performed by $P_i$ are same
- the sequence of values read and written by $P_i$ are the same
$E’$ for P1
$E’’$ for P1
First Important Observation
Lemma 1. If executions $E$ and $E’$ are indistinguishable to process $P_i$ then:
- If $P_i$ has not yet terminated, then $P_i$’s next step will be the same in any extension
- If $P_i$ has terminated, then $P_i$’s output is the same in $E$ and $E’$
Bivalent Executions
- Consider a (hypothetical) wait-free consensus protocol $A$
- Let $E$ be an execution of $A$
We say that $E$ is…
- $0$-valent if in every extension of $E$, all processes output $0$
- $1$-valent if in every extension of $E$, all processes output $1$
-
bivalent if there exist
- an extension $E’$ of $E$ in which all processes output $0$
- an extension $E’’$ of $E$ in which all processes output $1$
Second Important Observation
Lemma 2. Suppose $A$ solves consensus. Then there is a bivalent initial state.
- Here an initial state is an execution in which no process has yet taken a step
- the execution consists of only inputs for each process
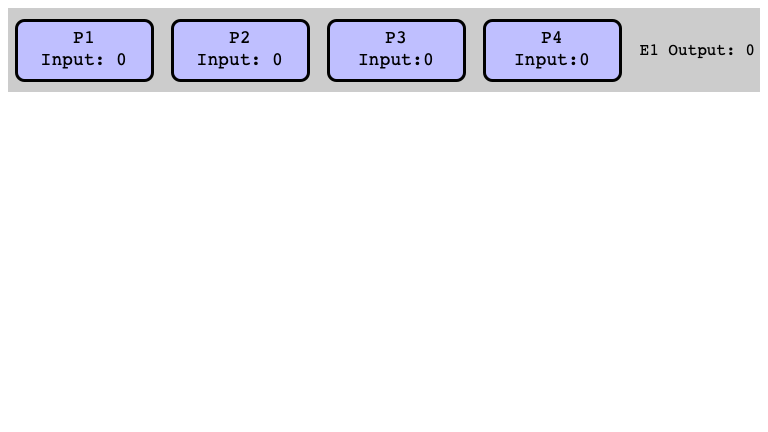
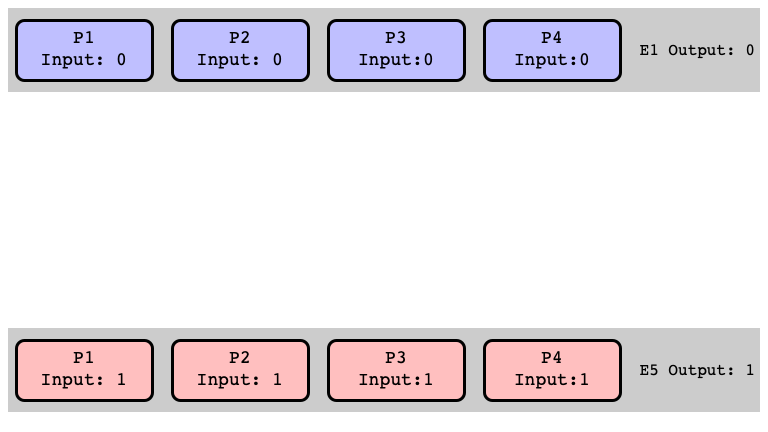
Proof of Lemma 2
Must show: there is a bivalent initial state
Argument:
- by contradiction: suppose no bivalent initial state
- consider sequence of initial states
- show some are $0$-valent, some are $1$-valent
- show that some must be bivalent
$E_1$ is $0$-valent (Why?)
$E_5$ is $1$-valent
More Initial States
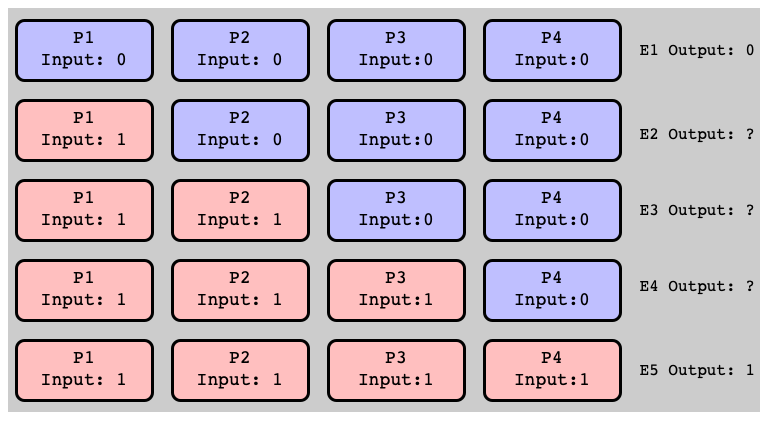
Assume: All Univalent
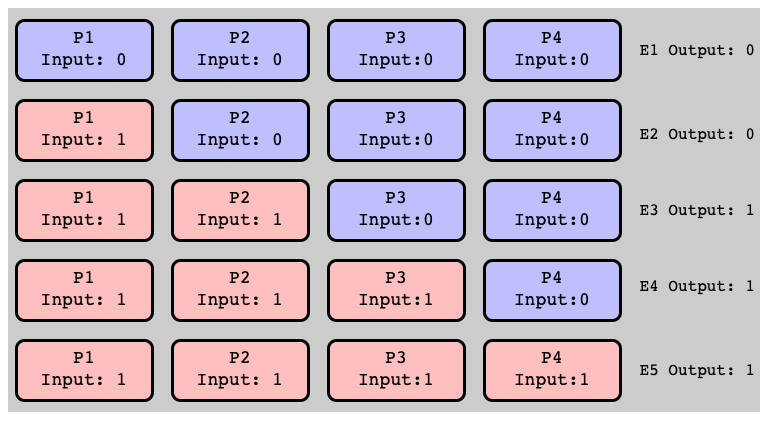
Adjacent Pair, Different Valency
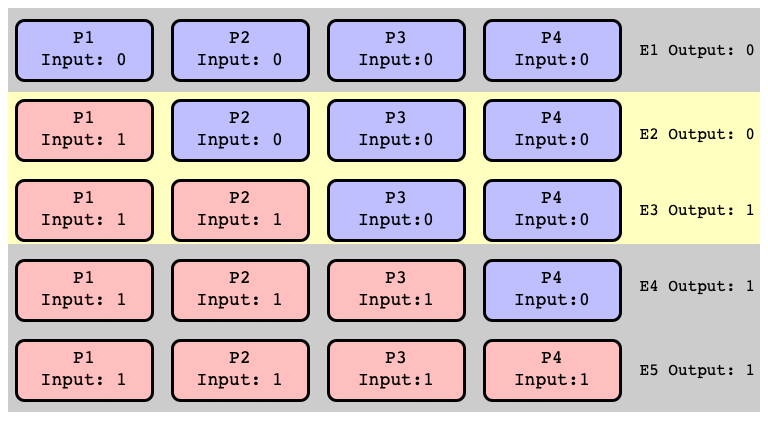
All Extensions of $E_2$ Return $0$
All Extensions of $E_3$ Return $1$
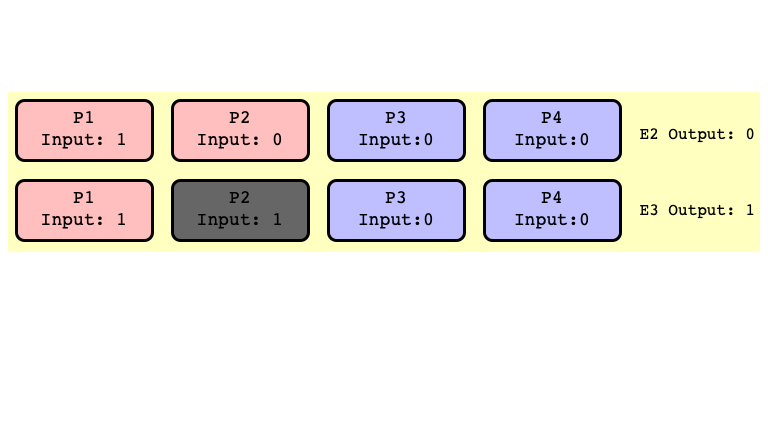
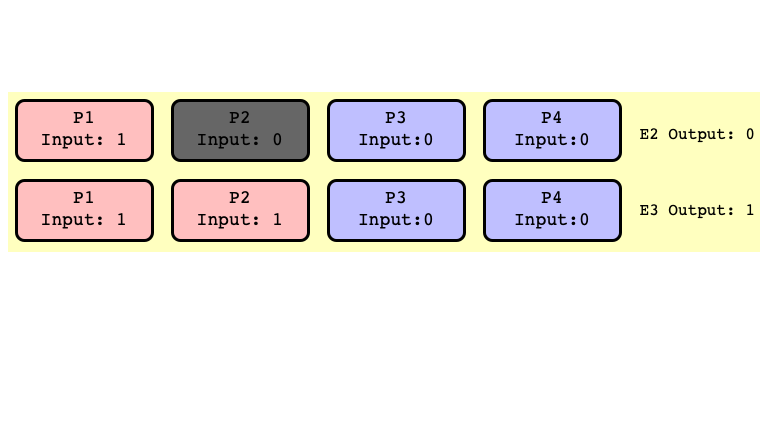
$E_2’$ and $E_3’$ Indistinguishable
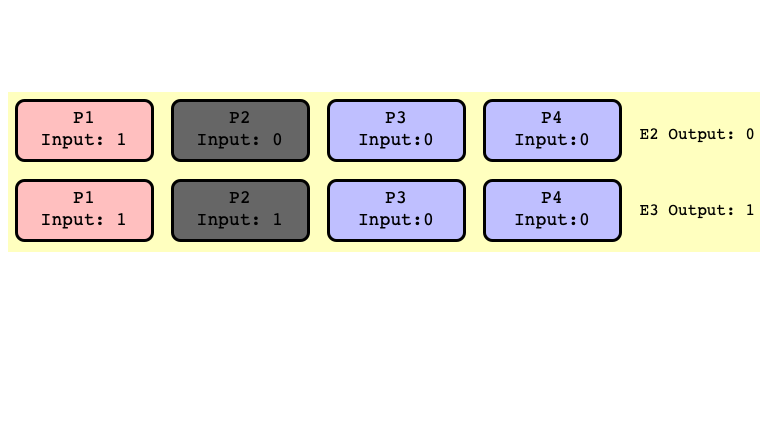
$E_2$ and $E_3$ Bivalent
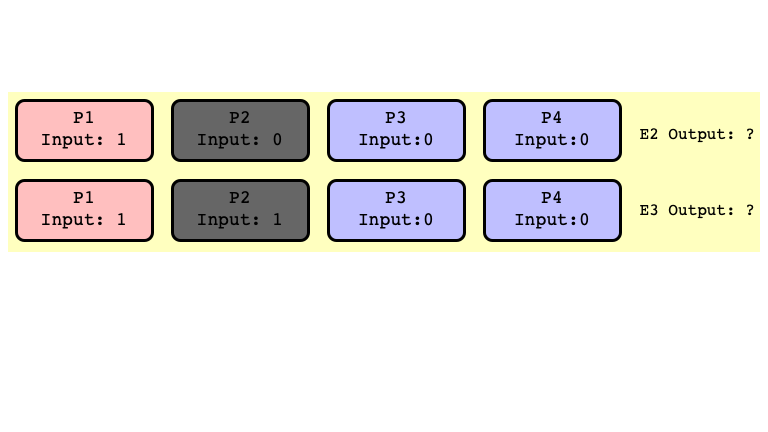
Note
Don’t need to assume $P_2$ crashes
- just assume first step of $P_2$ is scheduled after some other thread outputs
- this is possible because we assume $A$ is wait-free
- some process guaranteed to terminate even if one is not scheduled
Mere possibility of a crash together with wait-free assumption implies existence a bivalent initial state
- same holds if we require only termination with one fault
Next Time
- Bivalent initial conditions have critical executions
- Wait-free consensus is impossible!
- assuming only read/write registers…